Hierarchical core–shell structure of ZnO nanotube/MnO2 nanosheet arrays on a 3D graphene network as a high performance biosensing platform
Abstract
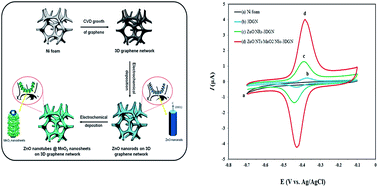
A hierarchical core–shell structure composed of ZnO nanotubes/MnO2 nanosheets was fabricated via a two-step electrochemical deposition procedure on the surface of a 3D graphene network (3DGN) as a free-standing monolithic electrode. In the first step, ZnO nanorod arrays were grown on the surface of a 3DGN followed by electrochemical deposition of MnO2 nanosheets in the next step, which caused the inner parts of initial ZnO nanorods to etch away and resulted in the formation of ZnO nanotubes (ZnO NTs). The highly porous interconnected graphene backbone offers very high conductivity and a large accessible surface area. On the other hand, the formation of ZnO nanotubes can enhance the electrode/electrolyte interface, while the porosity of MnO2 nanosheets is a great matrix for immobilizing biomolecules due to its good biocompatibility. The combination of these properties makes the prepared electrode a promising candidate for constructing biosensing platforms. As a proof of concept, the prepared composite electrode was used for the fabrication of a biosensor by immobilizing glucose oxidase (GOx) as a model enzyme and used for the detection of glucose. Amperometry results revealed very short response times. The obtained high sensitivity (3.9 mA μM−1 cm−2) and low detection limit (10 nM) for glucose exhibit that the proposed electrode provides a favorable platform for bioelectrochemical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...