Study on the interaction of berberine with nucleic acids in the presence of silver nanoparticles, and the fluorometric determination of nucleic acids†
Abstract
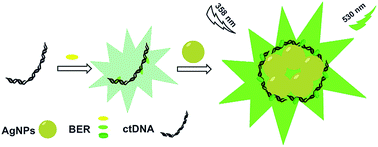
In this paper, the metal-enhanced fluorescence effect of AgNPs to berberine (BER) was found and applied in the sensitive determination of nucleic acids. Under optimum conditions, the enhanced fluorescence intensity of the system exhibited a linear response with concentrations of nucleic acids in the range of 4.0 × 10−8 to 6.0 × 10−6 g mL−1 for fish sperm DNA (fsDNA) and 1.0 × 10−8 to 4.0 × 10−6 g mL−1 for calf thymus DNA (ctDNA). Their corresponding detection limits (S/N = 3) are 21 ng mL−1 and 7.9 ng mL−1. This method had been successfully used to detect plasmid DNA in actual samples. In addition, the results of this study on the interaction mechanism of the system evidenced that the partial intercalation binding action between BER and ctDNA was strengthened by AgNPs. The ctDNA could induce the aggregation of AgNPs and provide an appropriate distance for BER and AgNPs, which resulted in the enhancement of the fluorescence intensity and the anti-photobleaching activity of BER.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...