Fe3O4@zirconium phosphate core–shell nanoparticles for pH-sensitive and magnetically guided drug delivery applications†
Abstract
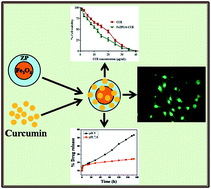
In the present study, biocompatible and magnetic Fe3O4@zirconium phosphate core–shell nanoparticles, comprising a magnetic Fe3O4 core and biocompatible zirconium phosphate shell, were prepared for pH-sensitive and magnetically guided drug delivery applications. The formation of the core–shell nanoparticles was affirmed from the XRD and FT-IR studies. TEM analysis revealed proper coverage of the zirconium phosphate shell on the magnetite core, while magnetic studies substantiated the superparamagnetic behavior of the nanoparticles. The suitability of the nanoparticles for intracellular application was validated through the conventional MTT assay, performed on human breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231). The loading-release behavior of the antitumor drug, curcumin, on and from the core–shell nanoparticles respectively were studied by UV-Vis spectroscopy, where the drug-loaded particles showed pH-sensitive release profiles. The nanoformulated curcumin was found to exhibit enhanced cytotoxicity and better bioavailability in contrast to native curcumin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...