The instability of S vacancies in Cu2ZnSnS4
Abstract
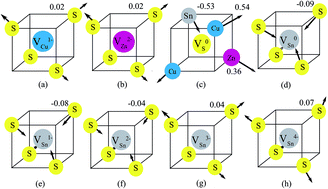
The electronic structures of the possible charge states of vacancies in the earth-abundant solar cell absorber material Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) are investigated using screened-exchange hybrid density functional theory. We find that all the charge states of anionic S vacancies (VS) are not stable because VS rehybridizes with the nearest neighbor Sn atom, reducing the valence of the Sn atom. Therefore, there is no charge transition level for VS. Instead, all the charge states of cation vacancies are stable. The copper and zinc vacancies show delocalized features which create shallow charge transition levels, while the tin vacancy shows localized feature which creates deep charge transition levels within the band gap and acts as a recombination center in CZTS.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...