Carbon dioxide capture by amino-functionalized ionic liquids: DFT based theoretical analysis substantiated by FT-IR investigation†
Abstract
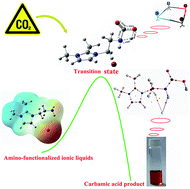
Carbon dioxide capture by amine-functionalized ionic liquids (IL), 1,2-dimethyl-(3-aminoethyl)imidazolium fluoride ([aEMMIM][F]), [aEMMIM][Cl], [aEMMIM][Br], and [aEMMIM][I] were synthesized and characterized by both DFT simulation and experimental methods. The most stable geometrical parameters of structures in this study were optimized at the B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level by employing the Gaussian09 program. The results showed that CO2 can be chemically captured in ILs by forming carbamic acid with a 1 : 1 molar ratio stoichiometry. DFT simulations were performed to investigate the configuration variations of the reactants, intermediates, transition states and products, as well as energy barriers and vibration frequency changes in the gas phase using the conductor-like polarizable continuum model (CPCM) in an aqueous solution. The vibration frequency obtained in DFT simulation was consistent with the experimental result by employing a scaling factor. AIM and NBO analysis were also carried out to investigate the nature and features of the studied structures at the molecular level.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...