A salification-induced charge transfer effect for improving the resistive memory performance of azo derivative-based devices†
Abstract
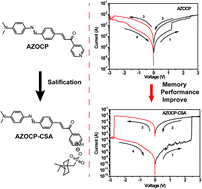
In this study, we report the synthesis of a new organic conjugate molecule, 3-(4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)phenyl)-1-(pyridin-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (AZOCP), and its camphorsulfonic acid salt (AZOCP–CSA). The photophysical and electrochemical characterization reveals that an enhanced π–π conjugation is formed in the camphorsulfonic acid salt because of the salification effect. The salification reaction also plays an important role in the formation of a more ordered stacking nanocrystalline film as evidenced by AFM and XRD analysis, and thus gives rise to an improved transport of charge carriers. The comparison of device performance demonstrates that the device based on the use of the salificated compound has better resistive memory behaviour in terms of ON/OFF ratio, retention time and rewritable cycle. Isothermal I–V correction and theoretical calculations confirm that the resistive performance is a result of an electric-field-induced charge transfer effect and the enhanced device performance of camphorsulfonic acid salt is due to the presence of a strong salification-induced charge transfer effect. Our experimental findings suggest that the simple but effective salification strategy may find widespread use in promoting performance of other organic resistive memory devices by introducing a strong charge transfer effect.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...