Cationic polymerization of p-methylstyrene in selected ionic liquids and polymerization mechanism†
Abstract
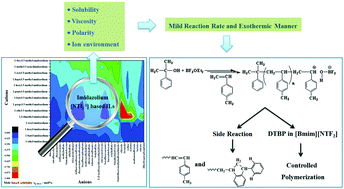
Cationic polymerization of p-methylstyrene (p-MeSt) in imidazolium-based [NTf2−1] ionic liquids (ILs) was investigated. The effects of the anions, cations, and alkyl chain length of ILs on p-MeSt solubility and viscosity were comprehensively studied. The COSMO-RS method, which is a valuable tool for screening and selecting ILs, was also applied to identify the most suitable solvent for p-MeSt cationic polymerization. The results revealed that p-MeSt cationic polymerization proceeded in a milder exothermic manner in ILs than in a traditional organic solvent. Controlled polymerizations were achieved in [Bmim][NTf2] with a CumOH/BF3OEt2 initiating system at −25 °C when 2,6-di-tert-butylpyridine was introduced. The cationic polymerization mechanism of p-MeSt in ILs was proposed on the basis of the results of density functional theory and the terminal structures of polymers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...