Talaroketals A and B, unusual bis(oxaphenalenone) spiro and fused ketals from the soil fungus Talaromyces stipitatus ATCC 10500†
Abstract
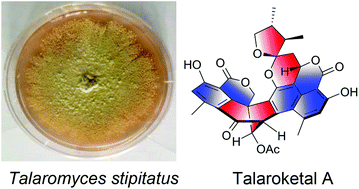
Two novel oxaphenalenone dimers, talaroketals A (2) and B (3), were isolated from the soil fungus Talaromyces stipitatus. Their structures and absolute configurations were determined on the basis of spectroscopic analyses, X-ray diffraction experiments and electronic circular dichroism. Compound (2) features a rare benzannulated 5,6-spiroketal ring system within the dimeric bis(oxaphenalenone) skeleton while the parent compound (3) harbors a fused bicyclic furano-pyran moiety. These two compounds may biogenetically result from the reaction of duclauxin with a dihydrofuran derivative of botryodiplodin. Additionally, talaroketals A (2) and B (3) display modest antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...