Comparing the strength of covalent bonds, intermolecular hydrogen bonds and other intermolecular interactions for organic molecules: X-ray diffraction data and quantum chemical calculations†
Abstract
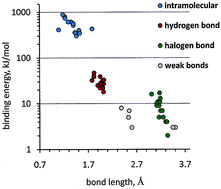
For each of the binding categories in the title, a survey of bond length data is made using the crystallographic information in the Cambridge Structural Database, yielding average values with standard deviations. For typical samples of each category, bond stretching energy curves are calculated ab initio using appropriate models, yielding expected equilibrium distances and stretching force constants. For the covalent chemical bond, X-ray and theoretical bond lengths coincide perfectly. For the hydrogen bond, the spread of experimental values around the averages is much larger, bond energies depend on the chemical environment, and vibrational energy spacings are of the order of a few RT units. For weak bonds of the C–H⋯X type or halogen bonds, the normalized distributions of experimental bond distances hardly show definite peaks, and stretching energy curves suggest a vibrational equipartition regime in which the room-temperature thermal bath is comparable with the dissociation limit. The results provide a quantitative picture of the relative strengths of the bonds in terms of reproducibility and hence predictability. Some aspects of organic crystal structure prediction and control are examined.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...