Bioavailability of catechins from guaraná (Paullinia cupana) and its effect on antioxidant enzymes and other oxidative stress markers in healthy human subjects†
Abstract
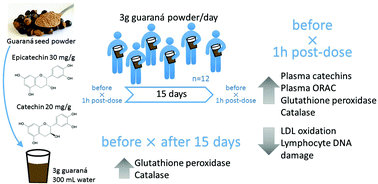
We assessed the effects of guaraná (Paullinia cupana) consumption on plasma catechins, erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activity (superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase) and biomarkers of oxidative stress (ex vivo LDL oxidation, plasma total antioxidant status and ORAC, and lymphocyte single cell gel electrophoresis) in healthy overweight subjects. Twelve participants completed a 15-day run-in period followed by a 15-day intervention with a daily intake of 3 g guaraná seed powder containing 90 mg (+)-catechin and 60 mg (−)-epicatechin. Blood samples were taken on the first and last day of the intervention period, fasting and 1 h post-dose. The administration of guaraná increased plasma ORAC, while reducing ex vivo LDL oxidation (only in the first study day) and hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage in lymphocytes, at 1 h post-dose. Plasma catechin (0.38 ± 0.12 and 0.44 ± 0.18 nmol mL−1), epicatechin (0.59 ± 0.18 and 0.64 ± 0.25 nmol mL−1) and their methylated metabolites were observed at 1 h post-dose but were almost negligible after overnight fasting. The activities of catalase (in both study days) and glutathione peroxidase (in the last intervention day) increased at 1 h post-dose. Furthermore, the activity of both enzymes remained higher than the basal levels in overnight-fasting individuals on the last intervention day, suggesting a prolonged effect of guaraná that continues even after plasma catechin clearance. In conclusion, guaraná catechins are bioavailable and contribute to reduce the oxidative stress of clinically healthy individuals, by direct antioxidant action of the absorbed phytochemicals and up-regulation of antioxidant/detoxifying enzymes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...