An update on dietary phenolic compounds in the prevention and management of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
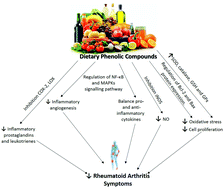
Certain nutritional components influence the cellular metabolism and interfere in the pathological inflammatory process, so that they may act as a coadjuvant in the treatment of many chronic inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Particularly, a wide range of evidence has demonstrated the beneficial roles of dietary phenolic compounds in RA because of their ability to modulate pro-oxidant and pro-inflammatory pathways reducing the onset of arthritic disease progression. These natural phenolic compounds can modulate both the action and the production of inflammatory mediators either directly or indirectly by modulating the action of other molecules involved in RA pathology. Subsequently, the purpose of this article is to review the main in vitro and in vivo studies in RA, which have documented interesting insights into the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties of dietary phenolic compounds focusing on their molecular action mechanisms involved in RA. The observations reported above are promising and suggest that the dietary phenolic compounds may influence the course of RA, ameliorating the RA symptoms and downregulating the inflammation at the molecular level; however, most of the studies conducted to date have been preclinical. Thus, future studies should therefore focus more on understanding the efficacy of these phenolic compounds in humans and bringing them to the forefront of the treatment of chronic human diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...