A highly effective and stable CuZn0.3MgxAlOy catalyst for the manufacture of chiral l-phenylalaninol: the role of Mg and its hydrotalcite-like precursor†
Abstract
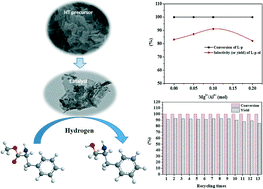
Highly effective CuZn0.3MgxAlOy (x = 0–0.2) catalysts for the synthesis of chiral L-phenylalaninol derived from Cu-rich hydrotalcite-like precursors were prepared by a co-precipitation method with Na2CO3 as the precipitant, and their physicochemical and catalytic properties were characterized. The results show that the presence of Mg2+ ions can promote the formation of hydrotalcite-like (htl) precursors, and the Mg2+ content would affect the phase purity of the prepared htl precursors. The BET surface area, exposed copper surface area and amount of acid sites of the samples decreased with the increase in the molar ratio of Mg2+/Al3+. Also, the dense layered htl precursors are beneficial to the atomically uniform distribution of the corresponding metal oxides in the prepared catalysts, promoting the stronger interaction between Cu0 and Al2O3 after the catalysts were reduced (SMSI effect). The activity of the CuZn0.3MgxAlOy catalysts is greatly dependent on not only the metallic copper surface area, but also the SMSI effect and the acidity of the catalysts. When Mg2+/Al3+ = 0.1 (mol), a phase-pure htl precursor could be obtained, and after calcination, the prepared CZA-0.1 catalyst exhibited very excellent catalytic performance for the hydrogenation of L-phenylalanine methyl ester to chiral L-phenylalaninol. After 5 h of reaction at 110 °C and 4 MPa H2, 100% conversion of L-phenylalanine methyl ester and 91.1% yield of L-phenylalaninol with an ee value of ~100% were achieved. After recycling 13 times, the L-phenylalaninol selectivity of the CZA-0.1 catalyst only decreased by 7.2%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...