Electronic transport properties of ultra-thin Ni and Ni–C nanowires
Abstract
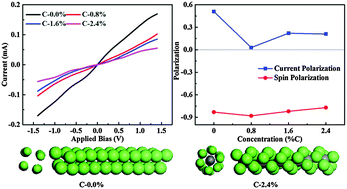
The structures and electronic transport properties of ultra-thin Ni and Ni–C nanowires obtained from carbon nanotube (CNT) templates are theoretically investigated. C atoms tend to locate at the central positions of nanowires and are surrounded by Ni atoms. Spin polarization at the Fermi level is not responsible for the spin filtration of these nanowires. Increasing C concentration can improve the resistance of nanowires by abating the number of electronic transmission channels and the coupling of electron orbitals between Ni atoms. Moreover, with the increase of diameter, the conductance of these nanowires increases as well. This study is helpful for guiding the synthesis of nanowires with desired applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...