Recodable surfaces based on switchable hydrogen bonds†
Abstract
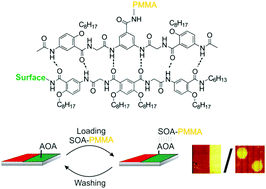
We introduce recodable surfaces solely based on reversible artificial hydrogen bonding interactions. We show that a symmetrical oligoamide (SOA) attached to poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) can be repeatedly immobilized and cleaved off spatially defined surface domains photochemically functionalized with asymmetric oligoamides (AOAs). The spatially resolved recodability is imaged and quantified via ToF-SIMS.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...