Electrochemical sensor based on a carbon paste electrode modified by graphene nanosheets and molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for determination of a chlordiazepoxide drug
Abstract
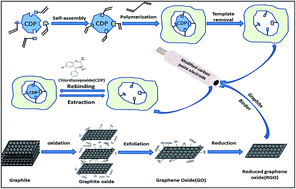
A selective and sensitive voltammetric sensor based on a graphene–carbon paste electrode (GCPE) modified with imprinted polymer nanoparticles (nano-MIP) for the determination of a chlordiazepoxide (CDP) drug has been developed. The chlordiazepoxide binding experiments indicated that the sensors modified by the nano-MIP have much higher adsorption ability for the CDP molecules than the non-imprinted polymer nanoparticle (nano-NIP) based sensor. Moreover, using graphene in the preparation of the CPE leads to a significant improvement in the response of the electrode to the CDP drug. The effect of the crosslinker type and amount of the template molecule on the MIP nanoparticles properties and other parameters affecting the sensor response were studied. Under optimized extraction and analysis conditions, the peak current obtained at the nano-MIP modified graphene–carbon paste electrode (nano-MIP-GCPE) was proportional to the chlordiazepoxide concentration within the range from 6.0 × 10−10 to 7.5 × 10−8 M (R2 = 0.9982) with a detection limit of 2.61 × 10−10 M. The repeatability of the developed sensor in terms of relative standard deviation was 3.2%. This sensor was successfully applied for the determination of chlordiazepoxide in pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluid samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...