Application of nucleic acid analogues as receptor layers for biosensors
Abstract
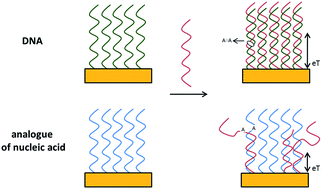
Nucleic acid-based biosensors are typically used to detect DNA or RNA fragments of clinical importance. Moreover, these sensors can also be used to detect different analytes, including viruses, peptides, small organic molecules and metal ions. However, the lack of resistance to restriction enzymes prevents the use of these sensors in in vivo measurements. Moreover, due to their reduced stability under environmental conditions as well as non-specific interactions, the usefulness of DNA biosensors can be limited. To mitigate these problems, analogues of nucleic acids can be used. These compounds are structurally similar to natural DNA, with alternative backbones. Due to their excellent affinity and specificity toward complementary strands, the most useful and popular nucleic acid analogues are peptide nucleic acid (PNA), locked nucleic acid (LNA) and phosphorothioate oligonucleotide (PTO). Herein, we present an overview of biosensors employing nucleic acid analogues as receptor layers, published in the last few years. Their advantages and their limitations are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...