Long cycle life of CoMn2O4 lithium ion battery anodes with high crystallinity†
Abstract
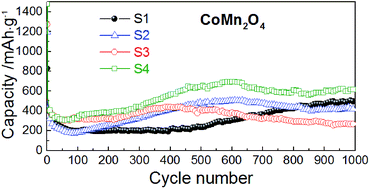
CoMn2O4 nanomaterials are prepared by a low temperature precipitation route employing metal acetates and NaOH. Structural changes, induced by different annealing temperatures, are comprehensively analyzed by X-ray powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. With rising annealing temperature the crystal lattice of CoMn2O4 undergoes changes; AO4 tetrahedra expand due to thermally induced substitution of Co2+ by larger Mn2+ metal ions on the A-site of the spinel structure, while in contrast, BO6 octahedra shrink since the B-site becomes partially occupied by smaller Co3+ metal ions on account of the migrated Mn ions. CoMn2O4 particle sizes are easily fine-tuned by applying different annealing temperatures; the particle size increases with increasing annealing temperature. During the battery operation, pulverization and reduction of particle sizes occurs regardless of the initial size of the particles, but the degree of division of the particles during the operation is dependent on the initial particle properties. Thus, contrary to the common assumption that nanostructuring of the anode material improves the battery performance, samples with the largest particle sizes exhibit excellent performance with a capacity retention of 104% after 1000 cycles (compared to the 2nd cycle).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...