The swim force as a body force
Abstract
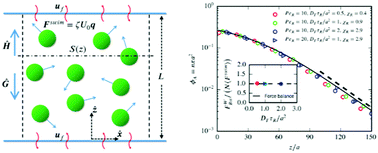
Net (as opposed to random) motion of active matter results from an average swim (or propulsive) force. It is shown that the average swim force acts like a body force – an internal body force. As a result, the particle-pressure exerted on a container wall is the sum of the swim pressure [Takatori et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2014, 113, 028103] and the ‘weight’ of the active particles. A continuum description is possible when variations occur on scales larger than the run length of the active particles and gives a Boltzmann-like distribution from a balance of the swim force and the swim pressure. Active particles may also display ‘action at a distance’ and accumulate adjacent to (or be depleted from) a boundary without any external forces. In the momentum balance for the suspension – the mixture of active particles plus fluid – only external body forces appear.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...