pH-Sensitive graphene oxide/sodium alginate/polyacrylamide nanocomposite semi-IPN hydrogel with improved mechanical strength
Abstract
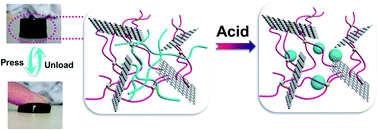
It is important and challenging to design a hydrogel that combines mechanical strength and stimuli responsiveness. In this study, graphene oxide (GO) was incorporated into the sodium alginate/polyacrylamide (SA/PAM) hydrogel as the reinforcement to promote the mechanical strength of the hydrogel. The hydrogel was prepared via in situ free-radical polymerization in the presence of SA with AM as the monomer and GO as the reinforcement, resulting in a GO/SA/PAM semi-interpenetrating polymer network (IPN). SA, cross-linking agent (N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide, BIS) and GO proportions were optimized to obtain a hydrogel with superior compressive strength. The GO18/SA0.1/PAM/BIS0.01 nanocomposite hydrogel (GO 18 mg, SA 0.1 g, BIS 0.01 g) displayed a compressive strength as high as 65.6 MPa at the compressive deformation of 80%. The hydrogel exhibited pH dependent swelling behavior and a maximum swelling ratio could be observed at pH 4 for the hydrogels with varied GO content. Moreover, the swelling behaviors of the semi-IPN hydrogels are dependent on the GO amounts, and the GO18/SA0.1/PAM/BIS0.01 hydrogel sample shows a lower swelling ratio due to its robust inner structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...