Immobilized lipase on porous ceramic monoliths for the production of sugar-derived oil gelling agent†
Abstract
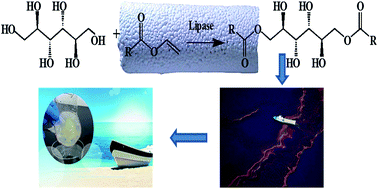
In this study, lipase from Candida sp. 99-125 was immobilized on glutaraldehyde-activated APTES-functionalized or epoxy-functionalized porous ceramic monoliths. The activity and stability of the immobilized lipases were investigated. The results indicated that the stabilities of immobilized lipases were improved significantly compared to native lipase. The immobilized lipases were used as catalysts for the production of oil gelling agent by using mannitol and fatty acid vinyl ester as substrates. Take Man-8 as an example, the yield of this oil gelling agent was more than 78% after 48 h reaction that catalyzed by the immobilized lipases. After the 5th batch reaction, more than 50% of yield can be maintained. Furthermore, the results of gelation tests indicated that the oil gelling agent can gel various hydrocarbons and oils. When the oil gelling agent was used to recover diesel from a biphasic mixture, more than 90% of the initial diesel can be recovered.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...