Effective catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorophenoxyacetic acids over Pd/graphitic carbon nitride†
Abstract
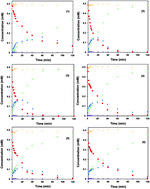
Catalytic hydrodechlorination (HDC) of chlorophenoxyacetic acids was performed over Pd/graphitic carbon nitride (Pd/g-C3N4) catalysts in the present work. A series of Pd/g-C3N4 catalysts were prepared by a deposition-precipitation method, and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption–desorption, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), CO chemisorption and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The Pd/g-C3N4 catalysts showed excellent activity to convert dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) into phenoxyacetic acid (PA) and the catalytic activity was correlated with the ratio of Pd2+/(Pd0 + Pd2+) and Pd particle size. In addition, HDC of 2,4-D over Pd/g-C3N4 catalyst followed the Langmuir–Hinshelwood model, indicating an adsorption-controlled mechanism. Other chlorophenoxyacetic acids, such as 2-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (2-CPA), 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (4-CPA) and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) could also be completely dechlorinated to PA over Pd/g-C3N4 catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...