Elucidation of the wettability of graphene through a multi-length-scale investigation approach†
Abstract
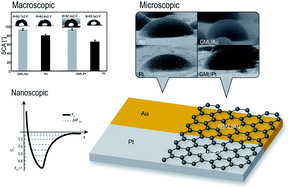
Univocal conclusions around the wettability of graphene exposed to environmental conditions remain elusive despite the recent efforts of several research groups. The main discrepancy rests on the question of whether a graphene monolayer (GML) is transparent or not to water and more generally what the role is that the substrate plays in determining the degree of wetting of the GML. In this work, we investigate the water transparency of GML by means of a multi-length-scale approach. We complement traditional static contact angle measurements and environmental scanning electron microscopy experiments with atomic force microscopy based force spectroscopy to assess the role that intermolecular interactions play in determining the wetting of GML. To gain deeper insight into the wetting transparency issue, we perform experiments on inert metals, such as gold and platinum, covered or not covered by GML. The comparison of the results obtained for different systems (i.e. GML covered and uncovered inert metals), provides unambiguous evidence that supports the non-wetting transparency theory of GML. This work aims to assist the development of technologies based on graphene–water interaction, such as graphitic membranes for water separation processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...