Enhanced power factor within graphene hybridized carbon aerogels†
Abstract
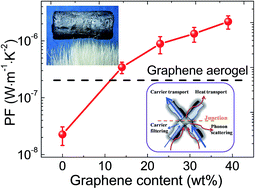
We demonstrate that the electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient can be simultaneously enhanced in graphene hybridized carbon aerogels (GHCAs). To prepare the GHCAs, graphene is introduced into the pyrolyzed resorcinol-formaldehyde (RF) aerogel, which significantly improves the electrical conductivity. At the same time, large interfaces between graphene sheets and pyrolyzed RF resin generate an energy filtering effect, which increases the Seebeck coefficient. This strategy promises a power factor which is two orders of magnitude higher than that of pure pyrolyzed RF aerogel. Moreover, the tenuous solid skeleton and highly open-cell foam structure of the GHCAs lead to ultra low thermal conductivity (0.06 W m−1 K−1) and apparent density (31 kg m−3). This may enable the development of a novel category of ultra-lightweight energy-conversion materials with thermal insulation capability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...