Rational design of a peptide capture agent for CXCL8 based on a model of the CXCL8:CXCR1 complex†
Abstract
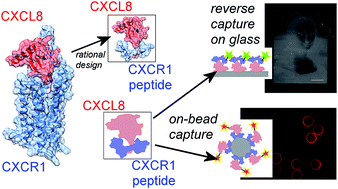
Protein-capture agents are widely used for the detection, immobilization and isolation of proteins and are the foundation for the development of in vitro diagnostic chips. The chemokine CXCL8 is an interesting protein target due to its involvement in the human inflammatory response. We constructed a novel structural model of CXCL8 interaction with its G-protein coupled receptor CXCR1, taking into account previously reported experimental data. From this CXCL8:CXCR1 model complex, the interaction of CXCL8 with residues near the extracellular domains 3 and 4 of CXCR1 were used as a scaffold for the rational design of a peptide capture agent called ‘IL8RPLoops’. A molecular dynamics simulation of IL8RPLoops indicates a stable helical conformation consistent with the CXCR1 structure from which it was derived. CXCL8 capture in fluorescence-based assays on beads and on glass demonstrates that IL8RPLoops is an effective capture agent for CXCL8. Additionally, we found IL8RPLoops to be a potent inhibitor of CXCL8-induced neutrophil migration and CXCL8:CXCR1 association. A theoretical binding model for IL8RPLoops:CXCL8 is proposed, which shows the peptide predominantly interacting with CXCL8 via electrostatic contacts with the ELR motif at the CXCL8 N-terminus.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...