Polysaccharide-assisted rapid exfoliation of graphite platelets into high quality water-dispersible graphene sheets†
Abstract
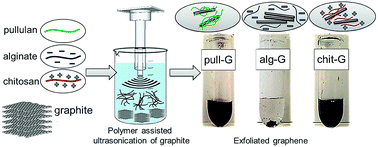
Ultrasound exfoliation of graphite with the assistance of three polysaccharides (nonionic pullulan, cationic chitosan, and anionic alginate) was investigated in this work. The effects of polymer type, initial concentration of graphite, and ultrasonication period on the graphene yield and quality were compared. Under a sonotrode-type ultrasonication treatment for 30 min, graphene aqueous dispersions with concentrations of up to 2.3 mg ml−1 in pullulan solutions and 5.5 mg ml−1 in chitosan solutions were achieved. The obtained graphene nanosheets were characterized as low-defect mono-layer, bi-layer, and few-layer (<5), and formed stable dispersions in water for up to 6 months. The adsorption of pullulan and chitosan biopolymers on the graphene surface as determined by TGA technique was approximately 2.5 wt% and 8.5 wt%, respectively, which accounts for the dispersibility and stability of the graphene sheets in water. Findings arising from this work suggest that pullulan and chitosan are more effective in exfoliating graphite into graphene than alginate due to the different surface free energy and thermodynamic affinity. The polysaccharide-assisted aqueous-exfoliation approach enables the production of water-dispersible graphene with high quality and large quantity, thus providing an industrially scalable route for new potential applications of graphene-based nanocomposites, e.g. in the food packaging industry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...