In situ photogalvanic acceleration of optofluidic kinetics: a new paradigm for advanced photocatalytic technologies†
Abstract
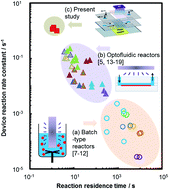
A multiscale-designed optofluidic reactor is demonstrated in this work, featuring an overall reaction rate constant of 1.32 s−1 for photocatalytic decolourization of methylene blue, which is an order of magnitude higher as compared to literature records. A novel performance-enhancement mechanism of microscale in situ photogalvanic acceleration was found to be the main reason for the superior optofluidic performance in the photocatalytic degradation of dyes as a model reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...