Study of chromium(vi) removal from aqueous solution using nitrogen-enriched activated carbon based bamboo processing residues
Abstract
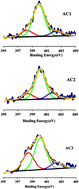
Nitrogen functional groups were introduced by urea and melamine onto the surface of two bamboo processing residues derived activated carbons (ACs) and Cr(VI) adsorption was investigated by changing various parameters. The results suggested that the incorporation of nitrogen species caused a visible increase in the adsorption capacity. The ACs with melamine and urea modification showed that the maximum removal of Cr(VI) from the solution having an initial Cr(VI) concentration of 100 mg L−1 was obtained at pH 2.0 as 89% and 85%, respectively. The adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) for unmodified AC was 78%. Langmuir adsorption model was applied to experimental equilibrium data of Cr(VI) adsorption and the adsorption kinetic followed pseudo-second-order model for these two ACs. Besides, the intraparticle diffusion kinetic model suggested the Cr(VI) adsorption could be divided into two phases: the diffusion controlled by external surface followed by an intra-particle diffusion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...