Controllable synthesis of a narrow polydispersity CO2-based oligo(carbonate-ether) tetraol†
Abstract
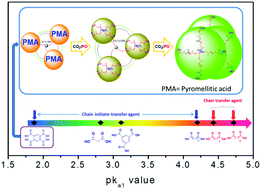
A CO2-based oligo(carbonate-ether) tetraol was synthesized in a controlled manner by immortal copolymerization of carbon dioxide (CO2) and propylene oxide (PO) in the presence of 1,2,4,5-benzenetetracarboxylic acid (btcH4) catalyzed by using a zinc–cobalt double metal cyanide (Zn–Co–DMC) catalyst. The number average molecular weight (Mn) of the tetraol was in a good linear relationship with the molar ratio of PO and btcH4 (PO/btcH4), and hence can be precisely controlled. Besides, the rapid chain transfer in immortal copolymerization afforded the tetraol with a narrow polydispersity index (PDI) of 1.08 at a Mn of 1400 g mol−1. Notably, the weight fraction of the byproduct propylene carbonate (WPC) was reduced to as low as 4.0 wt%, which is the lowest Wpc ever reported for the synthesis of branched polyols. The structure of the oligo(carbonate-ether) tetraol was confirmed, providing new evidence for the effect of the acidity (pKa1 value) of the chain transfer agent (CTA) on the initial catalytic mechanism. The acid only acts as the CTA directly participating in the copolymerization via the chain transfer reaction when its pKa1 value is higher than that of adipic acid (pKa1 = 4.43). However, when its pKa1 value is lower than that of succinic acid (pKa1 = 4.2), it acts as the initiate-transfer agent, which first initiates PO homopolymerization to an oligo-ether polyol, and then the in situ formed polyol acts as a new CTA for the copolymerization.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...