New dimeric carbazole–benzimidazole mixed ligands for the stabilization of human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA and as telomerase inhibitors. A remarkable influence of the spacer†
Abstract
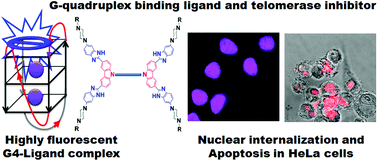
The development of G-quadruplex (G4) DNA binding small molecules has become an important strategy for selectively targeting cancer cells. Herein, we report the design and evolution of a new kind of carbazole-based benzimidazole dimers for their efficient telomerase inhibition activity. Spectroscopic titrations reveal the ligands high affinity toward the G4 DNA with significantly higher selectivity over duplex-DNA. The electrophoretic mobility shift assay shows that the ligands efficiently promote the formation of G4 DNA even at a lower concentration of the stabilizing K+ ions. The TRAP-LIG assay demonstrates the ligand's potential telomerase inhibition activity and also establishes that the activity proceeds via G4 DNA stabilization. An efficient nuclear internalization of the ligands in several common cancer cells (HeLa, HT1080, and A549) also enabled differentiation between normal HFF cells in co-cultures of cancer and normal ones. The ligands induce significant apoptotic response and antiproliferative activity toward cancer cells selectively when compared to the normal cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...