Enhanced anticancer potency using an acid-responsive ZnO-incorporated liposomal drug-delivery system†
Abstract
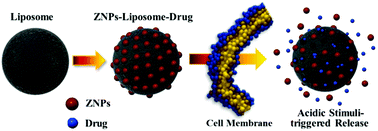
The development of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers is becoming important in chemotherapy. Liposomes, with an appropriate triggering mechanism, can efficiently deliver their encapsulated cargo in a controlled manner. We explored the use of acid-sensitive zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZNPs) as modulators of the responsive properties of liposomes. Nanocomplexes formed by the incorporation of ZNPs in liposomes (ZNP–liposomes) were designed to demonstrate the pH-responsive release of a drug (daunorubicin) without premature drug leakage and with the maintenance of the relevant therapeutic concentrations. The nanocomplexes were spherical in shape with a narrow size distribution and showed a high drug-encapsulating efficiency. Under acidic conditions, the ZNP–liposome nanocomplexes released the loaded drug more rapidly than bare liposomes. Using flow cytometry, confocal microscopy and an MTT assay, we demonstrated that these nanocomplexes were readily taken up by cancer cells, resulting in significantly enhanced cytotoxicity. On exposure to the acidic conditions inside cancer cells, the ZNPs rapidly decomposed, releasing the entrapped drug molecules from the ZNP–liposome nanocomplexes, producing widespread cytotoxic effects. The incorporated ZNPs were multimodal in that they not only resulted in a pH-responsive drug-delivery system, but they also had a synergistic chemo-photodynamic anticancer action. This design provides a significant step towards the development of multimodal liposome structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...