Extracting keratin from wool by using l-cysteine
Abstract
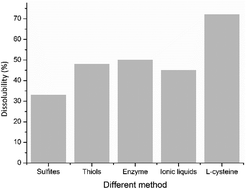
Keratin proteins are the major components of hair, feathers, wool and horns and represent an important source of renewable raw materials for many applications. The dissolution of the wool keratin is the first step of reuse of keratin wastes. In this work, L-cysteine was applied to the dissolution of wool keratin for the first time as a reducing agent. The dissolution time was 5 h at 75 °C with 72% dissolubility. XRD, ATR-FTIR and 13C NMR showed that the content of α-helix structures in regenerated wool keratin was decreased compared with natural wool. The content of S–S crosslinkages for regenerated wool keratin significantly decreased and broke about 62% of the S–S crosslinkages in the natural wool, as observed from Raman spectra.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...