Synergism in semiconducting nanocomposites: visible light photocatalysis towards the formation of C–S and C–N bonds†
Abstract
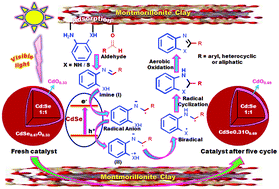
A simple, facile and visible light driven photochemical synthesis of 2-substituted benzothiazoles and 2-substituted benzimidazoles is achieved with CdSe nanocomposites as a photocatalyst. These nanocomposites are prepared by the molecular self assembly of 2–3 nm sized zinc blende CdSe phase within the layers of montmorillonite (MMT) through intercalation forming lamellar structure. CdSe/MMT exhibits excellent photocatalytic activity towards the synthesis of benzazoles using aliphatic, aromatic and heterocyclic aldehydes with better yields, and the efficiency is retained up to five cycles. XRD, XPS and Raman analyses of fresh and used CdSe/MMT reveal the passivation of structural defects due to the formation of a thin layer of CdO on the photocatalyst surface. The mixed phase of CdSe–CdO facilitates the generation of a hetero-junction on the CdSe/MMT surface, which is beneficial for photostability and sustainability. This process is also efficient under solar light and provides easy product isolation on the gram scale. Thus, it may be regarded as a greener methodology for the synthesis of bioactive scaffolds with excellent yields and high chemoselectivity using a tailor-made photocatalyst.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...