Efficient synthesis of quinoxalines from 2-nitroanilines and vicinal diols via a ruthenium-catalyzed hydrogen transfer strategy†
Abstract
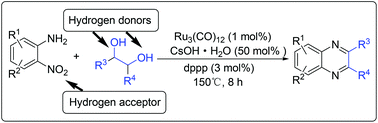
Via a ruthenium-catalyzed hydrogen transfer strategy, we have demonstrated a one-pot method for efficient synthesis of quinoxalines from 2-nitroanilines and biomass-derived vicinal diols for the first time. In such a synthetic protocol, the diols and the nitro group serve as the hydrogen suppliers and acceptors, respectively. Hence, there is no need for the use of external reducing agents. Moreover, it has the advantages of operational simplicity, broad substrate scope and the use of renewable reactants, offering an important basis for accessing various quinoxaline derivatives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...