Immobilization of l-aspartate oxidase from Sulfolobus tokodaii as a biocatalyst for resolution of aspartate solutions
Abstract
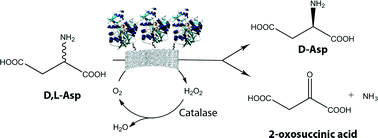
L-Aspartate oxidase from the thermophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus tokodaii (StLASPO) catalyzes the stereoselective oxidative deamination of L-aspartate to yield oxaloacetate, ammonia and hydrogen peroxide. The recombinant flavoenzyme shows distinctive features that make it attractive for biotechnological applications (it is highly thermostable, it is stable in a broad pH range, it tightly binds the FAD cofactor and it shows a low Km for dioxygen). In order to set up an efficient and economically feasible bioconversion process, in this work, we investigated the immobilization of this novel biocatalyst. The best results in terms of immobilization yield have been obtained when StLASPO was immobilized on the amino support Relizyme™ HA403/S R after activation with glutaraldehyde and on the epoxy support SEPABEADS® EC-EP/S (in both cases, through the free amino groups of the enzyme), as well as prepared as cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEA). By using the Relizyme™ HA403/S R support, as well as by the CLEA preparation procedure, full immobilization in terms of enzymatic activity was obtained. Immobilized StLASPO was used for the resolution of racemic solutions of 50 mM D,L-aspartate achieving full resolution in <1 hour. Indeed, the Relizyme-StLASPO immobilized enzyme (the one showing the highest immobilization yield) was efficiently reused in 5 cycles keeping full oxidation of L-aspartate in ≤2 hours. In a semi-preparative scale reaction, 66 mg of enantiomerically pure D-aspartate were produced in 1 day using 20 units of enzyme.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...