DFT+U studies of Cu doping and p-type compensation in crystalline and amorphous ZnS
Abstract
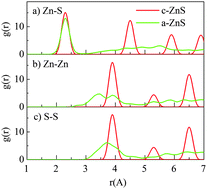
Zinc sulfide is an excellent candidate for the development of a p-type transparent conducting material that has great demands in solar energy and optoelectronic applications. Doping with Cu is one potential way to make ZnS p-type while preserving its optical transparency for the solar spectrum; however, this is limited by the extremely low solubility of Cu in ZnS and charge compensation mechanisms that eliminate the p-type characteristics. These mechanisms are different in crystalline (c-ZnS) and amorphous structures (a-ZnS), leading to different tendencies of doping Cu in these two ZnS phases, as well as the feasibility to form the p-type material. In this work, we have carried out fundamental studies of Cu doping in both c-ZnS and a-ZnS, using the continuous random network model and density functional theory with Hubbard's energy correction (DFT+U). The formation of a complex that contains two CuZn and one S vacancy is highly favorable in both phases. The local environment of this charge-compensated Cu complex obtained by DFT calculations agrees well with the previous EXAFS measurements. The incorporation of Cu into a-ZnS, on the one hand, is more tolerable compared to its crystal counterparts (zincblende), indicating possible higher Cu concentration. On the other hand, there is also another intrinsic mechanism to compensate the p-type characteristics in a-ZnS: the formation of the covalent S–S “dumbbell” units. This reconstruction of the local structure to form a S–S bond could occur spontaneously, thus making the p-type doping for ZnS challenging even in the amorphous phase.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...