Kinetic analysis of the reduction of 4-nitrophenol catalyzed by Au/Pd nanoalloys immobilized in spherical polyelectrolyte brushes†
Abstract
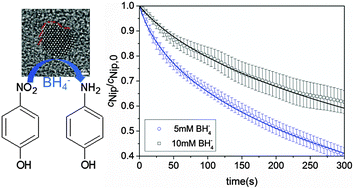
We present a detailed study of the catalytic activity of Au/Pd nanoalloys with Au : Pd molar ratio 75 : 25 synthesized using spherical polyelectrolyte brushes (SPB) as carrier system. The reduction of 4-nitrophenol (Nip) by sodium borohydride (BH4−) has been used as a model reaction. This reaction proceeds in two steps: 4-nitrophenol is first reduced to 4-hydroxylaminophenol which in a second step is reduced to the final product 4-aminophenol. Both steps of the reaction proceed on the surface of the nanoparticles (Langmuir–Hinshelwood-mechanism). We use this model to analyze the experimental data obtained by catalysis with the Au/Pd-nanoalloys. Good agreements between theory and experiments were found up to 30% conversion of Nip. The kinetic parameters were compared with the data derived from neat Au and Pd nanoparticles immobilized in the same SPB carrier system. The addition of 25% molar ratio of Pd to the nanoalloys increases the reaction rate of the first step nearly 10 times compared with that of SPB-Au and 60 times compared with that of SPB-Pd. Analysis of the nanoalloy by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy suggests that the surface defects of the nanoalloys play an important role for the enhanced catalytic activity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent advances in the chemical physics of nanoalloys

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...