Bio-coordination of bismuth in Helicobacter pylori revealed by immobilized metal affinity chromatography†
Abstract
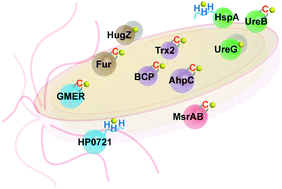
Over 300 Bi-binding peptides from 166 proteins in H. pylori were identified by Bi-IMAC. Bi3+ exhibits high selectivity towards peptide enriched by cysteines and histidines with dominated motif patterns of CXnC, CXnH and HXnH. Structural rationalization and functional categorization on the identified Bi-binding peptides and proteins provide an insight into the inhibitory action of bismuth drugs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...