Stabilization of cubic Sr2FeMoO6 through topochemical reduction†
Abstract
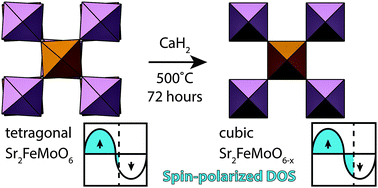
Sr2FeMoO6 has been extensively studied for application in spintronic devices. Through the topochemical de-intercalation of oxygen anions with metal hydride reduction, we demonstrate that the high temperature cubic phase is stabilized, at room temperature, whilst leaving the magnetic ordering intact. Synchrotron X-ray and neutron powder diffraction were used to characterize the structure and stoichiometry of the reduced oxide.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...