The effects of co-administration of butter on the absorption, metabolism and excretion of catechins in rats after oral administration of tea polyphenols
Abstract
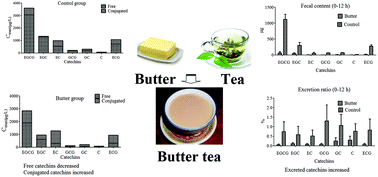
In Southwest China, tea polyphenols are usually utilized by way of butter tea. Tea polyphenols inhibit the absorption and biosynthesis of fatty acids in vivo, but the effects of butter on the pharmacokinetics of tea polyphenols have drawn less concern. A rapid UHPLC-MS/MS method was used to quantitatively determine the catechins in the plasma, feces and bile of rats after the oral administration of tea polyphenol or its combination with butter. In comparison with the single tea polyphenol treatment, the maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) of the free EGCG, EGC, EC, GCG, GC and ECG significantly decreased after the co-administration of butter. The mean residence times (MRT) of the free EGCG, EGC, EC, GC and ECG were also significantly prolonged. When the plasma samples were treated with β-glucuronidase and arylsulfatase, the pharmacokinetic parameters of the total catechins (free and conjugated forms) were not affected by the co-administration of butter. These results indicated that the total absorption of catechins was not affected by butter, but the metabolism of catechins had been changed. Furthermore, the fecal catechins were significantly increased by butter. The total fecal amount and excretion ratio of all catechins were increased highly. The biliary excretion of EGCG, EGC, EC, GCG and GC was significantly increased by the co-administration of butter. To sum up, the butter changed the metabolism of catechins in vivo by decreasing the plasma concentration of the free catechins but increasing the conjugated catechins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...