Melissa officinalis L. decoctions as functional beverages: a bioactive approach and chemical characterization
Abstract
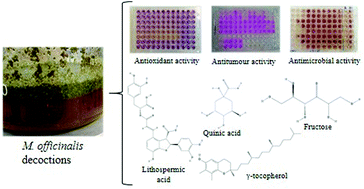
Lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.) is a member of the Lamiaceae family with a long story of human consumption. It has been consumed for decades, directly in food and as a decoction or an infusion for its medicinal purposes. In this manuscript, a detailed chemical characterization of the decoction of this plant is described, encompassing antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor activities. Rosmarinic acid and lithospermic acid A were the most abundant phenolic compounds. Quinic acid, fructose, glucose and γ-tocopherol were the most abundant within their groups of molecules. M. officinalis decoctions were active against a wide range of microorganisms, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium, and Penicillium funiculosum being the most sensitive bacteria and fungi, respectively. The growth inhibition of different human tumor cell lines (mainly MCF-7 and HepG2) was also observed, as also high free radical scavenging activity and reducing power. This manuscript highlights some beneficial effects of these functional beverages.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...