Consequences of hydrogen bonding on molecular organization and charge transport in molecular organic photovoltaic materials†
Abstract
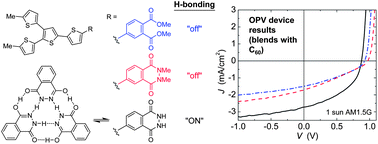
Reported is a systematic molecular structure–property relationship study to evaluate the consequences of dedicated H-bonding interactions between molecular electron donors on molecular assembly, absorption, charge collection, and performance in small-molecule bulk heterojunction organic photovoltaic devices. Three families of branched quaterthiophene donor chromophores have been synthesized with members that share nearly identical electronic and optical properties in the molecularly dispersed state but are either capable or incapable of self-association by hydrogen bonding (H-bonding). Phthalhydrazide-functionalized quaterthiophenes are H-bond “active” and show signatures of H-bond promoted assembly in solution (by 1H NMR) and in both neat and blended (with C60) films (by IR). Compared to control compounds with H-bonding “turned off”, the H-bonded derivatives show red-shifted thin film absorption (neat and as blends with C60), different colors as bulk solids, and increased decomposition and melt temperatures. Photovoltaic devices made from blends of H-bonded donor molecules with C60 as the electron acceptor show improved charge collection length and external quantum efficiency resulting in a more than two-fold enhancement in power conversion efficiency relative to non-H-bonding controls, from 0.49% to 1.04%. We anticipate this approach could be generalized to include other donor chromophores with lower optical gap to harvest more longer-wavelength photons and achieve higher power conversion efficiencies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...