Dynamics of self-propelled particles under strong confinement
Abstract
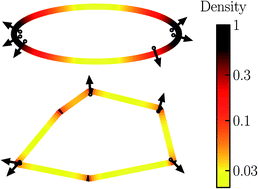
We develop a statistical theory for the dynamics of non-aligning, non-interacting self-propelled particles confined in a convex box in two dimensions. We find that when the size of the box is small compared to the persistence length of a particle's trajectory (strong confinement), the steady-state density is zero in the bulk and proportional to the local curvature on the boundary. Conversely, the theory may be used to construct the box shape that yields any desired density distribution on the boundary, thus offering a general tool to understand and design such confinements. When the curvature variations are small, we also predict the distribution of orientations at the boundary and the exponential decay of pressure as a function of box size recently observed in simulations in a spherical box.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...