Zn(ii) promoted dramatic enhancement in the enantioselective fluorescent recognition of functional chiral amines by a chiral aldehyde†
Abstract
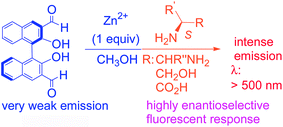
The addition of Zn2+ dramatically enhanced the enantioselective fluorescent responses of 3,3′-diformyl-1,1′-bi-2-naphthol toward chiral functional amines in methanol. One enantiomer of the chiral substrates, including diamines, amino alcohols and amino acids, was found to turn on the emission of this molecular probe at λ > 500 nm much more than the other enantiomer. This emission signal is greatly red-shifted from most of the other BINOL-based enantioselective fluorescent sensors whose fluorescent signals are generally at 400 ± 50 nm. Thus, a new window is opened for the use of BINOLs to observe chiral recognition events. The fluorescent responses of the new probe in the presence of Zn2+ toward a chiral diamine have also allowed a visual discrimination of these two enantiomers because of their different emitting color and intensity. The mass spectroscopic analyses for the reaction of the probe plus Zn2+ with the two enantiomers of a chiral diamine have revealed that the chirality match and mismatch between the probe and the substrate have produced different reaction products, generating very different fluorescent responses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...