Synthetic transporters for sulfate: a new method for the direct detection of lipid bilayer sulfate transport†
Abstract
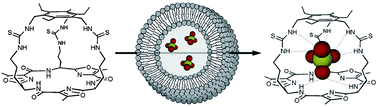
The transmembrane transport of anions by small synthetic molecules is a growing field in supramolecular chemistry and has focussed mainly on the transmembrane transport of chloride. On the other hand, the transport of the highly hydrophilic sulfate anion across lipid bilayers is much less developed, even though the inability to transport sulfate across cellular membranes has been linked to a variety of genetic diseases. Tris-thioureas possess high sulfate affinities and have been shown to be excellent chloride and bicarbonate transporters. Herein we report the sulfate transport abilities of a series of tris-ureas and tris-thioureas based on a tris(2-aminoethyl)amine or cyclopeptide scaffold. We have developed a new technique based on 33S NMR that can be used to monitor sulfate transport, using 33S-labelled sulfate and paramagnetic agents such as Mn2+ and Fe3+ to discriminate between intra- and extravesicular sulfate. Reasonable sulfate transport abilities were found for the reported tris-ureas and tris-thioureas, providing a starting point for the development of more powerful synthetic sulfate transporters that can be used in the treatment of certain channelopathies or as a model for biological sulfate transporters.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...