Highly selective NO2 sensor at room temperature based on nanocomposites of hierarchical nanosphere-like α-Fe2O3 and reduced graphene oxide
Abstract
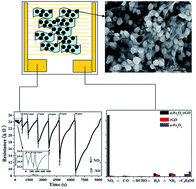
Nanosphere-like α-Fe2O3 modified reduced graphene oxide nanosheets were prepared by a simple hydrothermal method without any surfactant or template. The nanocomposites were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectra (RS), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques. The α-Fe2O3 nanospheres have a hierarchical structure, with diameter of about 40–50 nm, and grow uniformly on the surface of single graphene nanosheets. α-Fe2O3/rGO nanocomposites exhibit high response of 150.63% to 90 ppm NO2 at room temperature, 65.5 times higher than the response of pure graphene, and the detection limit for NO2 can be decreased down to 0.18 ppm. A mechanism is proposed for sensing of the nanocomposites: the high response of the nanocomposites to NO2 at room temperature is the synergistic effect of the two sensing materials and large specific surface area of the nanocomposites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...