Preparation and properties of highly stable quantum dot-based flexible silica films
Abstract
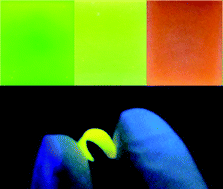
Highly luminescent hydrophobic CdSe and CdSe/CdxZn1−xS quantum dots (QDs) were synthesized via an organic route. The phase transfer of the QDs was carried out through a ligand exchange from 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APS) instead of an organic capping agent to get aqueous QDs. A functional sol–gel SiO2 sol with a high QD concentration was obtained from the aqueous QD colloidal solution with APS through the hydrolysis and condensation which subsequently occurred. Flexible inorganic SiO2 films with QDs were fabricated via various methods. The photodegradation experiments of the resulting films were completed. It is surprising that the QDs in films were revealed to be highly stable. Especially, the PL intensity of the films increased dramatically after irradiation by 365 nm UV light. By integrating a thin CdSe QD–silica film on a solar cell, the enhanced current demonstrated that a thin film can facilitate the continuous development of solar cells. Because of their high PL brightness, multicolor emission, flexibility and stability, these films will have great potential applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...