Near-infrared absorbing porphyrin dyes with perpendicularly extended π-conjugation for dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
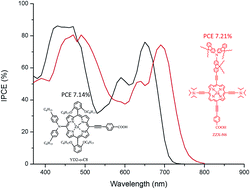
Two new porphyrin dyes, coded as ZZX-N6 and ZZX-N6C12, with photon-to-electron response up to 800 nm in the solar spectrum were synthesized for dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs). Four alkynyl groups were conjugated perpendicularly to the donor–π–acceptor axis of the porphyrins through triple bonds, resulting in 40–56 nm red-shift of absorption onset compared to porphyrin dye YD2-o-C8, leading to higher short-circuit current density. Post treatment of dye-coated TiO2 films by chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) with a concurrent increase of iodide concentration in an electrolyte improved the cell performance. Both impedance spectroscopic and photovoltage decay measurements showed that charge resistance at the TiO2–electrolyte interface increased after the CDCA treatment. Increasing iodide concentration in the electrolyte enhanced the reduction of I3− at the Pt counter electrode, leading to a higher short-circuit current density (JSC) and fill factor (FF). Under the optimized conditions, the ZZX-N6 based device exhibited an energy conversion efficiency of 7.21%, which is comparable to the YD2-o-C8 based device. The results demonstrate an alternative to broaden the light absorption capability of porphyrin dyes for high efficiency solar cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...