Hydroxysafflor yellow A induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells by blocking NFκB/p65 pathway and disrupting mitochondrial transmembrane potential
Abstract
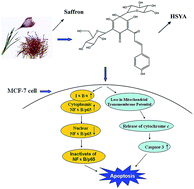
The molecular mechanisms and the possible effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) on the induction of apoptosis in the human breast cancer MCF-7 cells were investigated. The MTT assay showed that HSYA could specifically inhibit the growth of several solid tumor cells in a dose-dependent manner, especially in the MCF-7 cells. Analysis by flow cytometry indicated that the apoptosis of the MCF-7 cells increased after treatment with HSYA. Moreover, the ROS level increased, and the cell cycle was blocked when the MCF-7 cells were treated with HSYA. The HSYA-induced apoptosis involved Bax and p53 up-regulation, Bcl-2 and cyclin D1 down-regulation, release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria to the cytosol, activation of caspase-3, and disruption of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential (Δψm). In addition, HSYA could inhibit the NFκB/p65 pathway by blocking the NFκB/p65 nuclear translocation. We concluded that HSYA could induce apoptosis in MCF-7 cells and promote it through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...