Star-shaped POSS diblock copolymers and their self-assembled films
Abstract
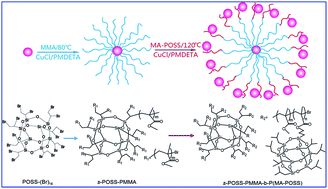
Novel 16-arm, star-shaped POSS-containing diblock copolymers are first synthesized by methylmethacrylate (MMA) and methacrylisobutyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (MA-POSS) using a cetylfunctional initiator of octakis(dibromoethyl) POSS (POSS-(Br)16). Three well-defined copolymers of s-POSS-PMMA277.3-b-P(MA-POSS)5.8,16.4,25.4 are discussed. The introduction of P(MA-POSS) could provide the copolymer with excellent hydrophobic/oleophobic performance and thermal stability. Although the size of core–shell micelles of s-POSS-PMMA277.3-b-P(MA-POSS)5.8–25.4 does not increase linearly with increasing MA-POSS content due to different self-assembly behaviors and steric effects, surface roughness (0.44–1.41 nm) and water–hexadecane contact angles (108°/50°–120°/58°) of films, as well as thermal stability (Td = 350–380 °C, Tg = 112–125 °C) and storage modulus (842–1600 MPa) of copolymers increased linearly. The effect of solvents on self-assembled micelles and films indicates that 340–370 nm core–shell micelles, 330–370 nm sun-like stretching micelles and 180–200 nm three-layer-structured micelles are formed in tetrahydrofuran (THF), chloroform (CHCl3) and butanone (MEK) solution, respectively. The lowest surface free energy (17.48 m Nm−1) is produced by film casting from THF solution due to the highest surface roughness (1.12 nm) and Si content (6.01%). While, the lowest water absorptive (Δm = 3800 ng cm−2) and viscoelastic (ΔD/Δf = −0.36) film is produced by CHCl3 solution, the film casting from MEK solution exhibits the highest water absorption (Δm = 6500 ng cm−2) and viscoelasticity (ΔD/Δf = −0.15). This is the first example of a 16-arm, star-shaped POSS diblock copolymers, and can be used as solvent-dependent coatings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...