Aligned carbon nanotube/copper sheets: a new electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction to hydrocarbons†
Abstract
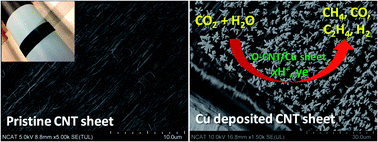
We controlled the morphologies of copper (Cu) nanostructure on aligned carbon nanotube (CNT) sheets, influencing the efficiency of the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2. Functionalized CNT sheets affected the pulsed electrodeposition of copper in terms of 3D growth, bonding, and electrochemical activity. CNT/Cu sheet electrocatalyst shows high performance in electrochemical reduction of CO2 to hydrocarbons at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Reduction products were carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), and ethylene (C2H4) gases. Carbon monoxide yields (178 μmol cm2 mA−1 h−1) and methane yields (346 μmol cm2 mA−1 h−1) at oxygen-plasma-treated CNT/Cu sheet electrodes were remarkably higher than other CNT/Cu and CNT sheets. Experimental results also show 3D morphology of copper growth on CNT sheets may play a critical role in hydrocarbon products from CO2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...